Skeletal muscle physiology
-

Depending on the relationship that an individual establishes with external resistances, muscle activation can lead to three different contractions: CONCENTRIC: With shortening of muscle fibers. Overcoming external resistance. The external force acts in the opposite direction to the movement. ECCENTRIC: With lengthening of muscle fibers. Assignment to external resistance. The external force acts in the…
-
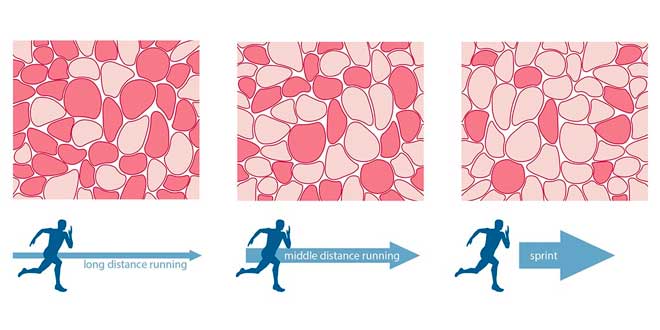
Skeletal muscle is a tissue capable of making a wide range of functional demands, from performing highly precise movements for which little force is required, to maximum contractions, to maintaining the body’s posture. This versatility is due, in part, to the existence of several types of muscle cells or fibers, which have different functional, metabolic…
-
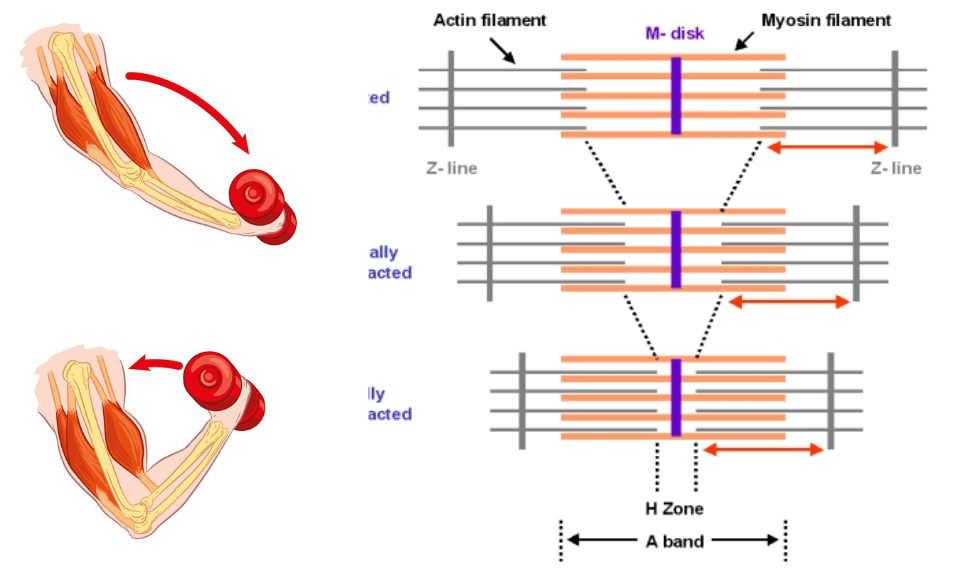
At rest, the thin and thick filaments of a sarcomere slightly overlap. During contraction, the thin and thick filaments slide past each other bringing the Z lines closer to the center of the sarcomere. Contraction is stimulated when the muscle fiber innervating α motor neuron releases the neurotransmitter acetylcholine as a consequence of an action…
-
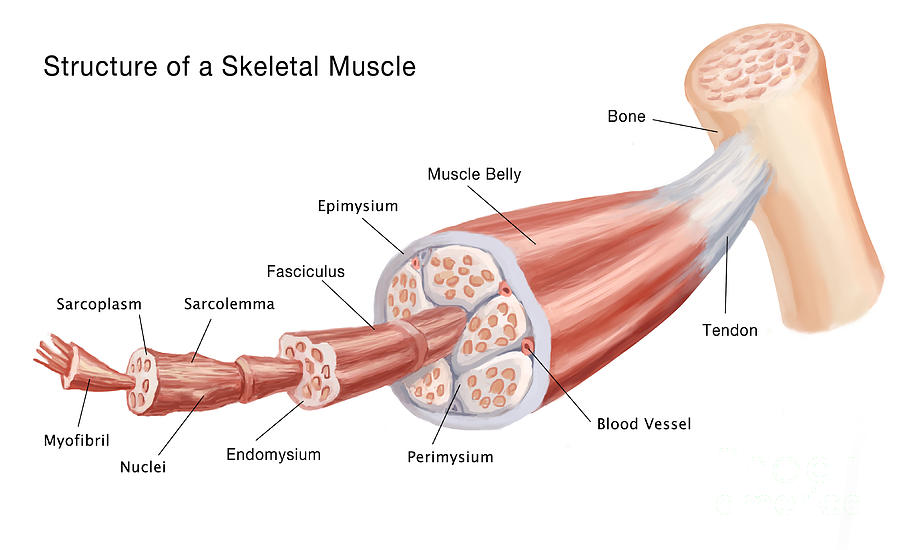
The human body contains approximately 650 muscles and the different sets of muscles are enveloped by a membrane of connective tissue called the fascia (e.g., thoracolumbar fascia). The functional and structural unit of muscle tissue is the muscle fiber, differentiated muscle cell or myocyte. Each muscle fiber is surrounded by a fine network of reticular…
